So, you’re wiring a 50-amp appliance—maybe a new oven, a hot tub, or an EV charger? A crucial question is, “What size wire do I need?” This guide covers everything about wiring a 50-amp circuit, from understanding the NEC and ampacity to choosing between copper and aluminum wiring. We’ll also explain how distance affects your wire choice, cover common 50-amp applications, and offer troubleshooting tips. By the end, you’ll confidently choose the right wire size for your project.
Quick Answer: Wire Size for a 50-Amp Breaker
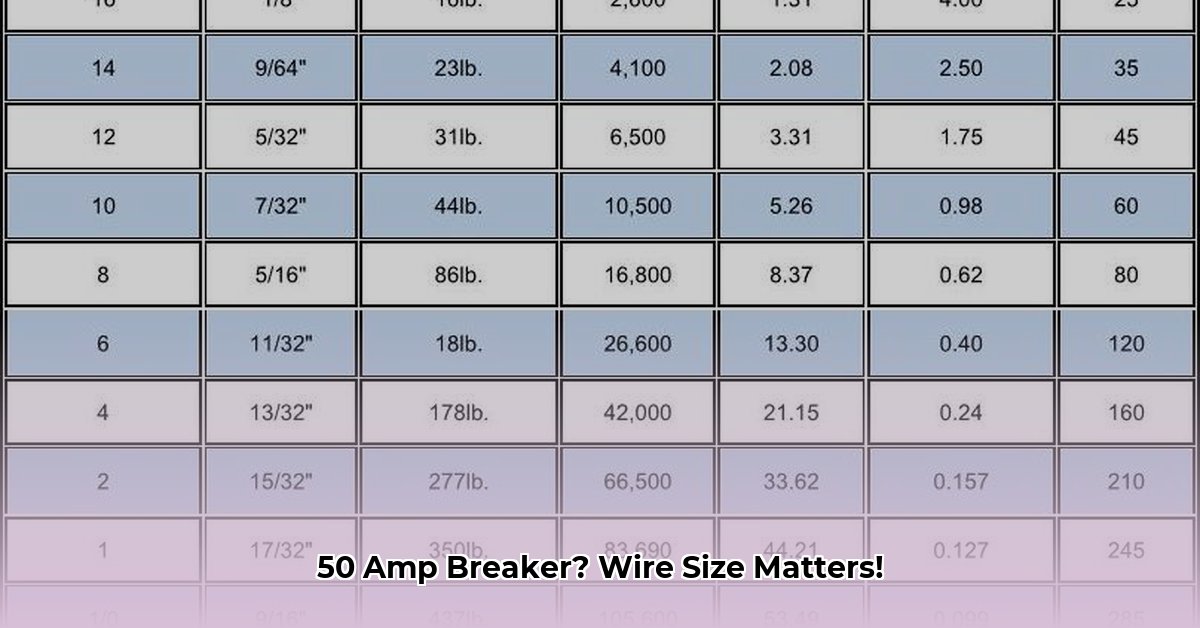
Need the answer fast? For runs under 100 feet, 6 AWG copper or 4 AWG aluminum wire is likely sufficient. Longer distances require thicker wire to prevent voltage drop. See the table below, but keep reading for the why and other essential information.
| Material | Wire Gauge (AWG) | Distance (feet) |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | 6 | Up to 100 |
| Copper | 4 | 100-200 (and beyond, but calculations are key) |
| Aluminum | 4 | Up to 100 |
| Aluminum | 2 | 100-200 (and beyond, calculations are key) |
Decoding the NEC and Ampacity
The National Electrical Code (NEC) is the rulebook for safe electrical installations. A key concept is ampacity—the maximum current a wire can safely carry. The NEC’s 80% rule suggests a continuous load shouldn’t exceed 80% of the breaker’s rating. For your 50-amp breaker, that’s 40 amps. This safety buffer prevents overheating.
Copper vs. Aluminum: Wiring Face-Off
Choosing between copper and aluminum is like choosing between a truck and a van—both work, but have different strengths. Copper offers better conductivity, allowing for smaller gauge wire. Aluminum is lighter and cheaper but requires special connectors.
| Feature | Copper | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Durability | Higher | Lower |
| Installation | Easier | More complex |
Voltage Drop: Why Distance Is Key
Voltage drop is the decrease in voltage as electricity travels. Longer wires, with higher resistance, cause greater voltage drop. This is why longer runs need thicker wires (lower AWG) to minimize this loss. Online voltage drop calculators can help determine the correct size. [Link to a reputable voltage drop calculator]
Cable Types for 50-Amp Circuits
Different cables suit different applications. THHN and THWN are common for indoor use, while UF-B is suitable for outdoor or underground installations. SER and SEU are often used for service entrances. Mobile home feeder cables cater to specific needs.
Common 50-Amp Applications
50-amp circuits power appliances like ranges, ovens, HVAC units, welders, and EV chargers.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Unmarked wire? Don’t guess. Consult a qualified electrician. Suspect voltage drop? A multimeter can confirm. Safety first!
Safety First: Consult a Pro
This guide is informational, not a substitute for professional advice. Consult a licensed electrician for all electrical work. Local codes vary, so always check before starting a project.
Wire Size by Distance: A Deeper Dive
Choosing the right wire gauge isn’t one-size-fits-all. While 6 AWG copper or 4 AWG aluminum works for shorter runs (under 100 feet), longer distances require thicker wires to combat voltage drop.
| Distance | Copper Wire Gauge | Aluminum Wire Gauge | Why Thicker Wire? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under 100 ft | 6 AWG | 4 AWG | Standard for common applications |
| 100-150 ft | 4 AWG | 2 AWG | Minimizes voltage drop |
| 150-200 ft | 3 AWG | 1 AWG | Further reduces voltage drop |
| Over 200 ft | Consult NEC | Consult NEC | Specialized calculations needed |
Factors affecting wire size:
- Ambient Temperature: Higher temperatures increase resistance, requiring potentially larger gauge wires.
- Continuous vs. Non-Continuous Loads: Continuous loads (like refrigerators) require larger wires than occasional loads (like power tools).
- Cable Type: Different cable types have different temperature ratings and ampacity, influencing the appropriate gauge.
Copper vs. Aluminum: A Detailed Look
Choosing between copper and aluminum involves balancing cost, performance, and safety.
Copper:
- Pros: Excellent conductivity, durability, corrosion resistance.
- Cons: Higher cost.
Aluminum:
- Pros: Lower cost, lightweight.
- Cons: Lower conductivity (requiring larger gauge), susceptibility to corrosion (needing special connectors), thermal expansion (potentially loosening connections).
Understanding Voltage Drop and Its Impact
Voltage drop, the loss of electrical potential over distance, can significantly affect appliance performance. A 3% drop might seem minor, but it can cause overheating and premature wear. Larger drops (5% or more) can lead to noticeable issues.
How to calculate voltage drop:
While a formula exists (Vd = (2 * K * L * I) / CM for single-phase), online voltage drop calculators simplify the process. Input your wire length, current, and material to get the recommended gauge. Future research may offer further insights into minimizing voltage drop.
Choosing the Right Cable
There are different cable types for 50-amp circuits:
- THHN, THWN: Common for indoor installations within conduit or raceways.
- NM-B (Romex): Common for indoor wiring within walls.
- UF-B: Suitable for direct burial underground or outdoor exposure.
- SER, SEU: Used for service entrance cables, connecting your home to the power grid.
- Mobile Home Feeder: Specifically designed for mobile home applications.
Choosing the correct type depends on the environment and application.
Safety and Professional Consultation
While this guide provides valuable information, it does not replace professional advice. Always consult a licensed electrician for any electrical work. Electricity is dangerous, and safety should be the top priority. This article is for informational purposes only, and I am not liable for any issues arising from its use. Always check local electrical codes and regulations before starting any project. Ongoing research in electrical safety and technology means guidelines and best practices can evolve. Stay informed, stay safe!
- Dora the Explorer Wipe-Off Fun: Safe & Mess-Free Activities for Little Explorers - April 18, 2025
- Does Lemongrass Repel Mosquitoes? Fact vs. Fiction + How to Use It - April 18, 2025
- Do Woodchucks Climb Trees?Fact vs. Fiction - April 18, 2025