Dive into the pedagogical principles of curriculum construction with our comprehensive guide, tailored specifically for B.Ed. notes. In this article, we’ll elucidate the foundational theories, methodologies, and best practices that underpin the development of transformative and engaging learning experiences.
Key Takeaways:
- Curriculum construction requires systematic planning and integration of knowledge.
- Key principles guide curriculum development, ensuring alignment with students’ needs and learning outcomes.
- Principles include suitability to age, student interests, environmental relevance, comprehensiveness, correlation, practical work, flexibility, forward-looking perspective, teacher involvement, and collaboration.
Principles of Curriculum Construction: B.Ed. Notes
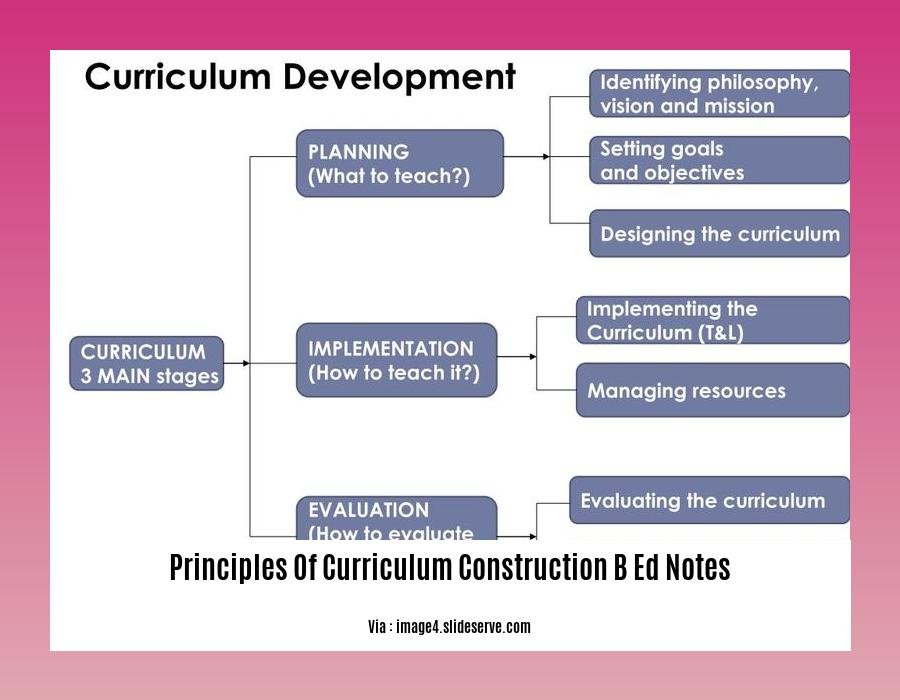
Hey there, future educators! Let’s dive into the fascinating world of curriculum construction. It’s like building a bridge between learning goals and student success. And to do it right, you need to master the principles of curriculum construction. These principles guide every step of the curriculum development process, ensuring your lessons are engaging, effective, and aligned with your students’ needs.
H3: The Core Principles
1. Age and Mental Level Suitability:
Your curriculum should match the developmental stage and cognitive abilities of your students. Picture this: trying to teach calculus to kindergarteners won’t be a fruitful endeavor!
2. Student Interests:
Hook ’em! Consider your students’ passions and interests to design lessons that resonate with them. Think “science through storytelling” or “math through real-life scenarios.”
3. Environmental Centricity:
Connect your curriculum to the world around your students. Foster environmental awareness by incorporating local history, geography, and current events.
4. Comprehensive Coverage:
Your curriculum should encompass all essential subjects and areas of knowledge. It’s like a well-rounded meal that nourishes all parts of the learner’s mind.
5. Correlation:
Interconnect your subjects! Help students see the big picture by showing how different subjects relate to each other. It’s like the puzzle pieces of knowledge coming together.
6. Practical Work:
Give your students a hands-on experience. Design projects, experiments, and activities that allow them to apply their knowledge in real-life situations.
7. Flexibility:
Expect the unexpected! Your curriculum should be adaptable to changing circumstances and student feedback. It’s like a rubber band that can stretch and contract to meet the needs of the classroom.
8. Future-Forward:
Don’t get stuck in the past! Anticipate future trends and emerging technologies in your curriculum design. Prepare your students for the world they’ll live in tomorrow.
9. Teacher Consultation:
Tap into the wisdom of your fellow educators! Involve teachers in the curriculum development process to gather their practical insights and ensure the curriculum works in the classroom.
10. Collaborative Effort:
Curriculum construction is not a solo act. Encourage collaboration between educators, administrators, and stakeholders to create a curriculum that reflects the needs of the entire educational community.
Remember, these principles are your guiding light in the curriculum construction journey. They’ll help you design transformational learning experiences that ignite your students’ passion for knowledge!
Are you worried about the high cost of constructing a polyhouse? Get all the details you need on polyhouse construction cost to plan your budget effectively.
Tired of dealing with shoddy workmanship on construction projects? Find out how to spot poor construction workmanship and protect your investment.
Looking for reliable construction companies in Port Elizabeth? Explore our comprehensive list of Port Elizabeth construction companies to find the perfect match for your project.
Ensure a clean and hygienic construction site with portable toilet construction sites. Learn about the benefits and regulations for implementing these essential facilities.
Streamline your project management by understanding the key principles of time table construction. Discover how to create realistic schedules and avoid costly delays.
Instructional Design and Pedagogical Approaches

In the dynamic landscape of education, ** Instructional Design and Pedagogical Approaches serve as the cornerstone of effective curriculum development**. These principles guide educators in crafting transformative learning experiences that foster student engagement and academic success.
Alignment with Learning Outcomes
Effective curriculum design aligns pedagogical approaches with specific learning objectives. By establishing clear and measurable learning goals, educators can design instruction that directly targets the desired student outcomes. This alignment forms the foundation for effective teaching and assessment practices.
Significance of Pedagogical Frameworks
Pedagogical frameworks provide a theoretical foundation for curriculum design. They define the beliefs, values, and philosophies that shape educational practices. By understanding these frameworks, educators can make informed decisions about teaching methods, content selection, and assessment strategies.
Incorporating Educational Research
Advancements in educational neuroscience have shed light on the cognitive processes involved in learning. This research informs instructional design by providing evidence-based strategies for engaging students, promoting memory formation, and developing higher-order thinking skills.
Implementing Differentiated Learning
Differentiated instruction recognizes the diverse learning needs and styles of students. By providing multiple entry points, flexible pacing, and varied learning activities, educators can cater to the individual needs of each learner, ensuring equitable access to high-quality education.
Key Takeaways:
- Instructional Design and Pedagogical Approaches are essential for effective curriculum development.
- Alignment with learning outcomes is crucial for targeted instruction.
- Pedagogical frameworks provide a theoretical foundation for educational practices.
- Educational research informs evidence-based instructional strategies.
- Differentiated learning addresses the diverse learning needs of students.
References:
- Principles of Curriculum Design
- [Understanding the Principles of Curriculum and Instructional Pedagogical](
Curriculum Evaluation and Assessment Techniques
Hey there, curriculum explorers!
When it comes to building a curriculum that sticks, evaluation and assessment are your trusty sidekicks. They help you gauge if your teachings are hitting the mark and if your students are soaking up the knowledge. So, let’s dive into these techniques and elevate your curriculum to new heights!
Assessment Techniques: Finding the Right Fit
Assessment isn’t just about slapping a grade on a paper; it’s about gathering evidence of your students’ learning. You’ve got a toolbox full of techniques at your disposal:
-
Formal Assessments: Tests, quizzes, and exams. Standardized, structured, and usually time-bound – they paint a clear picture of student understanding.
-
Informal Assessments: Observations, discussions, and portfolios. Flexible and ongoing, they provide valuable insights into your students’ learning journey.
-
Formative Assessments: Quick check-ins and feedback sessions. Help students identify areas for improvement and refine their understanding.
-
Summative Assessments: Evaluate student learning at the end of a unit or course. Sum up their overall progress and help you plan for the future.
Evaluation: Getting the Measure of Your Curriculum
Now, evaluation is a step back, a deeper look at the big picture. It’s about assessing the effectiveness of your entire curriculum. Ask yourself:
-
Alignment to Objectives: Do your lessons line up with the learning goals you’ve set?
-
Student Engagement: Are students actively participating and finding value in the curriculum?
-
Data Analysis: Use qualitative and quantitative data to identify areas for improvement.
-
Stakeholder Feedback: Gather input from students, parents, and colleagues to refine your curriculum.
Key Takeaways:
- Assessment and evaluation are essential for improving student learning.
- Choose assessment techniques that align with your learning objectives.
- Use evaluation to refine your curriculum and ensure effectiveness.
- Involve stakeholders in the evaluation process for valuable feedback.
Sources:
- Educational Assessment
- Curriculum Evaluation and Improvement
Emerging Trends and Innovation in Curriculum Construction
Within the realm of curriculum construction, there’s an exciting buzz surrounding emerging trends and innovation.
Student-Centered Learning: It’s all about active student engagement, empowering them to co-create learning experiences that resonate with their individuality.
Transnational Influence: The world is a global classroom. Curriculum now reflects international frameworks, fostering global perspectives.
Curriculum Innovation: It’s not just about tweaking, but rethinking and creating fresh solutions. Think of it as a problem-solving adventure.
Educational Neuroscience: This is the power of science in the classroom. Research-based insights shape curriculum design to enhance learning experiences.
Key Takeaways:
- Student-centered learning puts learners at the helm of their educational journey.
- Transnational influence widens horizons and fosters global understanding.
- Curriculum innovation invites educators to think outside the box.
- Educational neuroscience leverages brain-based research for effective curriculum design.
Sources:
- Emerging Trends and Innovations in Curriculum Development
- Principles of Curriculum Design and Construction Based on the Concepts
FAQ
Q1: What is the principle of relevance in the context of curriculum construction?
Q2: How does the principle of flexibility support the adaptation of the curriculum to the individual needs of students?
Q3: Explain the significance of the principle of balance in curriculum construction and how it ensures harmonious learning experiences.
Q4: What role does the principle of correlation play in fostering interdisciplinary connections and knowledge application?
Q5: How does the principle of student-centered learning empower students and promote their engagement in the learning process?
- Are Daffodils Perennials?A Complete Guide to Planting & Care - March 31, 2025
- Are Carpenter Bees Dangerous? Stings, Damage, and Control - March 31, 2025
- How to Get Rid of Ants in the Washroom: A Complete Guide - March 31, 2025










