[- Asset Reconstruction Companies in India: Driving Financial Resurgence -] As the Indian financial sector gallops ahead, the role of asset reconstruction companies (ARCs) has been gaining prominence.
Key takeaways:
- ARCs purchase non-performing assets from banks and aim to recover them.
- ARCs are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Existing ARCs in India include ARCIL, ASREC, and Edelweiss.
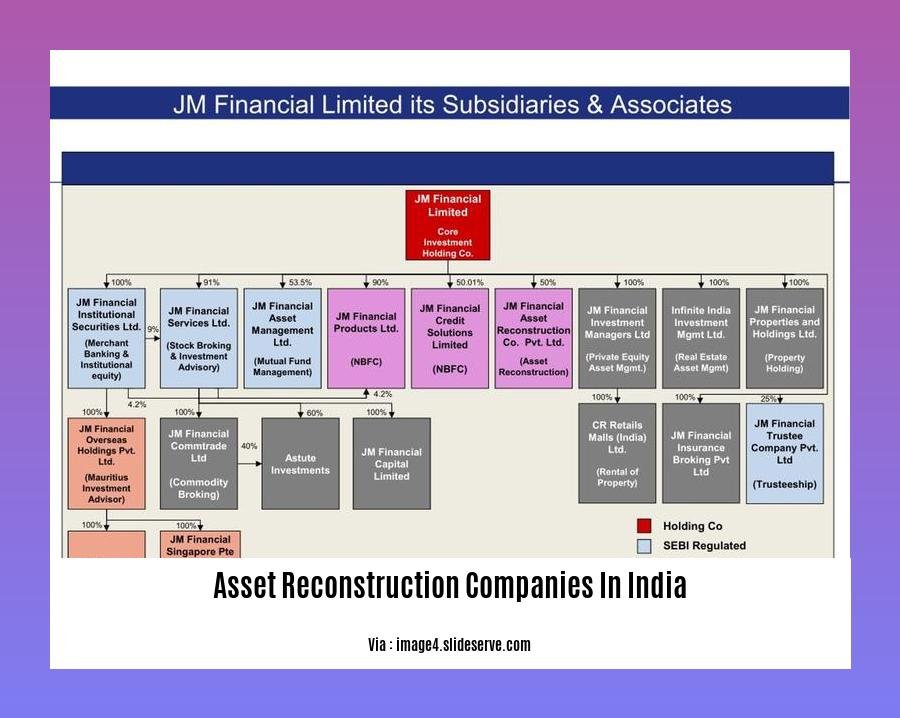
Asset Reconstruction Companies in India

What are Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs)?
ARCs are specialized financial institutions that play a crucial role in India’s financial system. They acquire non-performing assets (NPAs) and stressed assets from banks and financial institutions. By doing so, ARCs help clean up banks’ balance sheets and free up capital for lending.
The Role of ARCs
ARCs work in various ways to recover and improve the value of acquired assets. They employ a range of strategies, including:
- Restructuring loans: Working with borrowers to modify loan terms and make them more manageable.
- Selling assets: Selling acquired assets to third-party buyers or through auctions.
- Redeveloping properties: Investing in distressed properties to improve their value and marketability.
Regulation of ARCs
ARCs are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which ensures their compliance with regulatory guidelines. RBI monitors ARCs‘ activities and financial performance to safeguard the interests of investors and other stakeholders.
Benefits of ARCs
- Improved financial health of banks: ARCs help banks reduce their NPA levels, which improves their financial stability.
- Increased availability of credit: By freeing up capital in banks, ARCs enable banks to lend more, supporting economic growth.
- Enhanced asset recovery: ARCs‘ expertise in asset recovery helps maximize the value of acquired assets, benefiting all stakeholders.
Challenges Faced by ARCs
- Acquiring quality assets: It can be challenging for ARCs to acquire high-quality assets at reasonable prices.
- Legal and regulatory issues: ARCs must navigate complex legal and regulatory frameworks, which can sometimes hinder their operations.
- Competition from other recovery mechanisms: ARCs face competition from other entities, such as banks’ own asset recovery units and private equity firms.
Outlook for ARCs
The future of ARCs in India looks promising. The government’s focus on reducing NPAs and the growing distress in the real estate sector are creating ample opportunities for ARCs. By leveraging their expertise and adopting innovative strategies, ARCs can continue to play a vital role in the financial resurgence of India.
-
To swiftly resolve conflicts in the construction industry, explore our comprehensive guide on alternative dispute resolution.
-
Ensure the well-being of workers on construction sites by implementing effective safety and health measures detailed in our article on applying safety and health.
-
For reliable reconstruction services, consider our esteemed reconstruction companies that have a proven track record of excellence.
-
Find the perfect partner for your reconstruction project in India by browsing our directory of reconstruction companies that meet your specific needs.
Challenges Faced by ARCs in India

Navigating the financial landscape in India, ARCs have a pivotal role in addressing non-performing assets. Despite their importance, they encounter significant challenges that hinder their operations.
Acquisition Hurdles:
Sourcing quality assets is a major challenge for ARCs. Banks often cherry-pick the best assets, leaving ARCs with a limited pool to choose from. The lack of access to auctions and due diligence on prospective sellers further complicates the acquisition process.
Regulatory and Legal Maze:
ARCs operate in a complex web of regulations and laws. The adherence to these frameworks can be cumbersome, leading to delays and increased compliance costs. Moreover, the legal process for enforcing contracts and recovering assets can be lengthy and unpredictable.
Competitive Landscape:
ARCs face fierce competition from distressed asset funds and special situation investors. These rivals often have deeper pockets and more flexible mandates, making it challenging for ARCs to acquire and manage assets effectively.
Economic Downturns and Slow Recovery:
Amidst economic setbacks, the supply of stressed assets tends to increase. However, ARCs face challenges in disposing of these assets during prolonged downturns. Slow recovery affects demand, leading to lower asset valuations and reduced returns.
Key Takeaways:
- The acquisition of quality assets is a key challenge for ARCs due to limited access to auctions and due diligence.
- Navigating a complex regulatory and legal environment can lead to delays and increased compliance costs for ARCs.
- Fierce competition from other investors makes it challenging for ARCs to acquire and manage assets effectively.
- Economic downturns and slow recovery can impact the supply and demand of stressed assets, affecting ARC performance.
Sources:
- How ARCs are solving India’s bad loan problem
- Reserve Bank of India – Asset Reconstruction Companies
Growth and evolution of ARCs in India
For years, non-performing assets (NPAs) have been a major concern for the Indian banking system. In response to this challenge, the government established Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) under the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act (SARFAESI Act) of 2002.
How ARCs work:
ARCs acquire distressed assets, including loans and properties, from banks and financial institutions. By restructuring, managing, and recovering value from these assets, ARCs help reduce the burden of NPAs on the financial system.
Steps involved in the ARC process:
– Acquisition: ARCs purchase stressed or non-performing assets from banks.
– Due diligence: They evaluate and assess the acquired assets to determine their recovery potential.
– Management: ARCs develop and implement strategies to recover value from the assets, such as loan restructuring, asset sales, and property redevelopment.
– Exit: The recovered value is distributed among stakeholders, including creditors, investors, and the ARC itself.
Benefits of ARCs:
– Reduced NPA burden on banks
– Improved financial health of the banking system
– Increased availability of credit
– Enhanced asset recovery
Challenges faced by ARCs:
– Availability of quality assets
– Legal and regulatory complexities
– Competition from other recovery mechanisms
Conclusion:
ARCs have played a significant role in the growth and evolution of the Indian financial sector. By addressing the issue of non-performing assets, they have contributed to the overall health and stability of the banking system. The government’s recent initiatives and RBI guidelines aim to further strengthen the ARC ecosystem and promote their continued growth and effectiveness.
Key Takeaways:
- The growth and evolution of ARCs in India have been crucial in addressing the NPA challenge.
- ARCs acquire and manage distressed assets, helping to clean up bank balance sheets and free up capital.
- They employ various strategies to recover value from acquired assets, contributing to the financial health of banks and the broader economy.
- ARCs face challenges such as the availability of quality assets and regulatory complexities, but ongoing efforts are being made to address these issues.
Relevant URL Sources:
- Asset Reconstruction Companies: An Analysis of Growth and Evolution
- Reserve Bank of India – Asset Reconstruction Companies
Future Outlook for ARCs in India
The future outlook for ARCs in India appears promising due to several factors:
- Government initiatives: The Indian government is actively supporting the growth of ARCs to address the issue of NPAs in the banking sector.
- RBI’s revised guidelines: The RBI’s recent guidelines aim to strengthen the governance, disclosures, and balance sheets of ARCs, making them more robust.
- Increasing NPA levels: The surge in NPAs due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the ongoing economic slowdown has created a significant opportunity for ARCs to acquire and resolve distressed assets.
- Growing demand for ARC services: Banks and financial institutions are increasingly seeking the services of ARCs to manage their NPAs effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- ARCs play a critical role in resolving NPAs in the Indian banking sector.
- Future outlook for ARCs in India is promising due to government support, RBI guidelines, and increasing demand for their services.
- ARCs contribute to financial stability by assisting banks in cleaning up their balance sheets and freeing up capital for lending.
References:
- Revised RBI Guidelines to Structurally Strengthen ARCs
- How ARCs are solving India’s NPA crisis
FAQ
Q1: What is the purpose of Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) in India?
A1: ARCs play a crucial role in the Indian economy by assisting banks in resolving distressed assets, freeing up capital for lending and contributing to overall financial stability.
Q2: How do ARCs acquire distressed assets?
A2: ARCs typically acquire stressed or non-performing assets from banks and financial institutions by purchasing these assets through various mechanisms such as purchase or securitization.
Q3: What are the benefits of using ARCs to resolve NPAs?
A3: The involvement of ARCs in NPA resolution has several benefits, including reduced risk for banks, an increase in their lending capacity, improved financial stability, and the freeing up of capital for more productive purposes.
Q4: Are there any challenges faced by ARCs in India?
A4: While ARCs have been successful in resolving NPAs, they do face challenges, a major one being the availability of funding, as they often require significant capital to acquire and manage distressed assets.
Q5: How does the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulate ARCs?
A5: ARCs in India are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which sets guidelines and standards for their operations. The RBI also monitors the performance of ARCs to ensure compliance and foster a healthy and transparent ecosystem.
- The Best Battery Picture Lamps for Effortless Artwork Illumination - April 1, 2025
- Double Sink Bath Vanity Tops: A Buyer’s Guide - April 1, 2025
- Bath Towel Measurements: A Complete Guide to Choosing the Right Size - April 1, 2025