Step into the realm of home electrical wiring with our Comprehensive Guide to Home Wiring Color Codes. Unravel the mysteries of electrical circuits as we decode the vibrant hues of wires that illuminate your abode. Discover the secrets behind the colors, unraveling their significance in ensuring safety and compliance with the National Electrical Code. Embark on a journey through the world of wire gauges, insulation types, and grounding techniques, gaining invaluable insights into the art of residential wiring.
Key Takeaways:
- Neutral: White or Gray
- Ground: Bare Copper, Green, or Green with Yellow Stripe
- Hot to Outlet: Black
- Hot 240V or Wall-Switched: Red
- Hot for Fans and Multi-Way Switches: Blue and Yellow
- NEC-Mandated Colors: Neutral (White/Gray), Ground (Bare Copper/Green)
- Phase Wiring: Black (Phase 1), Red (Phase 2), Blue (Phase 3)
- Wire Gauge and Color: White (14 AWG), Yellow (12 AWG), Orange (10 AWG), Black (8 or 6 AWG)
Home Wiring Color Code: A Guide to Electrical Safety
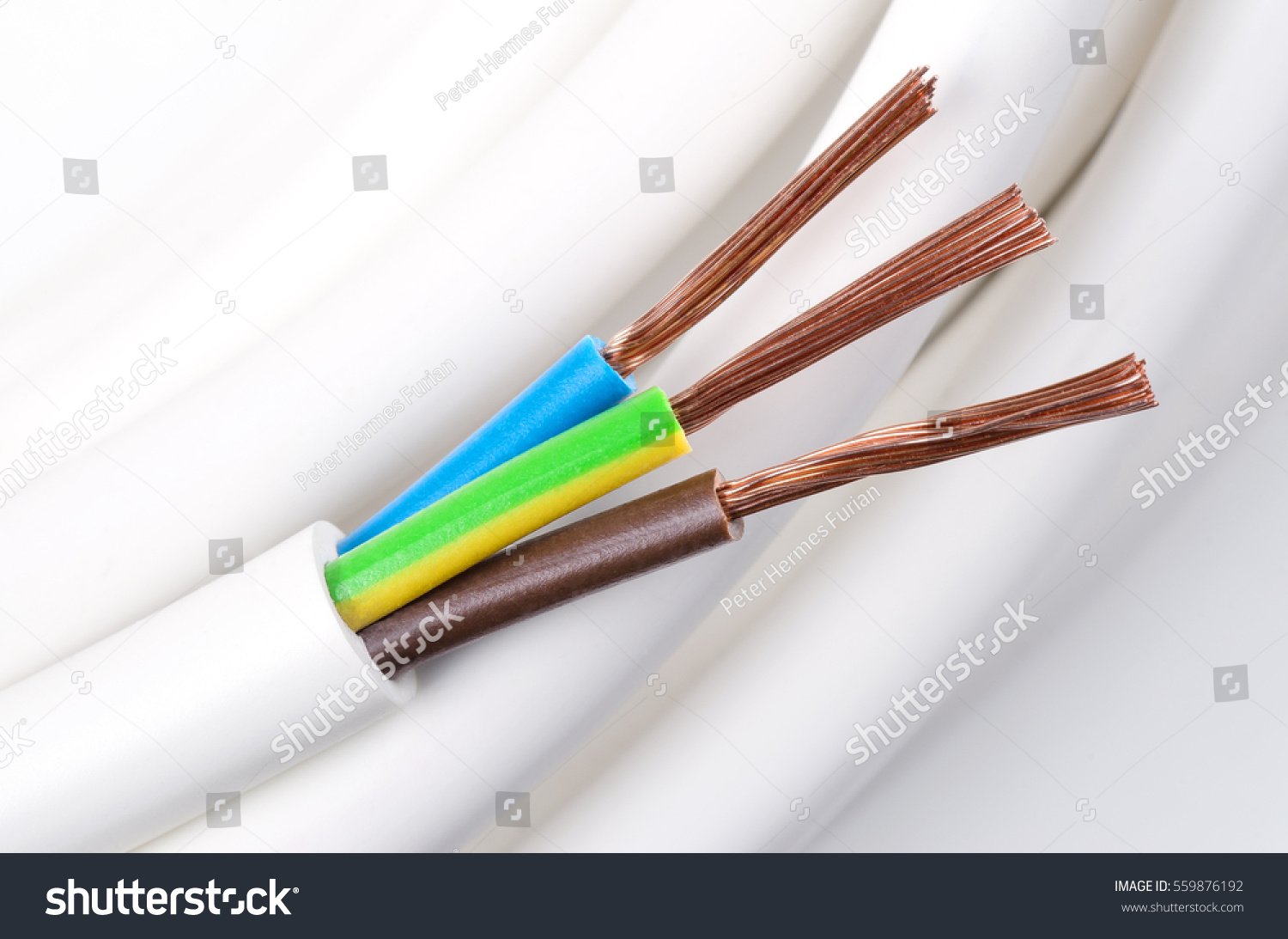

Understanding home wiring color code is crucial for safe and efficient electrical installations. Here’s a simplified guide to help you navigate the world of electrical wiring:
Understanding Color Codes
White or Gray: Indicates the neutral conductor. Connects to the silver screw on outlets and switches.
Bare Copper or Green: Ground wire. Connects to the green screw on outlets and switches, providing a safety path for excess electricity.
Green with Yellow Stripe: Also a ground wire. Used in newer installations for added safety.
Black: Hot wire. Supplies power to outlets and switches from a circuit breaker panel. Connects to the brass screw on outlets and switches.
Red: Hot wire. Typically used in 240-volt outlets or controlled by a wall switch.
Blue and Yellow: Hot wires used for ceiling fans and multi-way switches.
Mandatory Colors
The National Electrical Code (NEC) mandates the following colors:
- White or Gray for neutral conductors
- Bare Copper or Green for ground wires
Breakdown by Amperage
The color of insulated wires also indicates wire gauge and amperage:
| Color | Wire Gauge | Amperage |
|---|---|---|
| White | 14 AWG | 15 A |
| Yellow | 12 AWG | 20 A |
| Orange | 10 AWG | 30 A |
| Black | 8 or 6 AWG | 40 A |
Tips for Home Wiring
- Always follow the NEC when working with electrical wiring.
- Use the correct wire gauge for the amperage of the circuit.
- Ground all electrical circuits properly for safety.
- Label circuits clearly for easy identification and troubleshooting.
- Hire a licensed electrician for complex or high-voltage electrical work.
- To increase your chances of winning at home, check out our comprehensive guide on the home winning odds.
- Ensure the safety of your home electrical system by following our detailed instructions on home wiring code.
- Support your child’s academic progress with our age-appropriate home work for class 3.
- Achieve your fitness goals with our downloadable home workout plan PDF tailored to your convenience.
Understanding Hot Wires and Their Designations
Key Takeaways:
- Black wires are commonly designated as hot wires.
- Hot wires carry current from the electrical panel to appliances or devices.
- The National Electrical Code (NEC) does not mandate specific colors for hot wires, but black is the most commonly used.
- Hot wires provide the electrical power necessary for equipment to operate.
- If not handled appropriately, hot wires can pose electrical hazards.
- Other colors, such as red or white wires with black or red tape, may also indicate hot wires.
Hot wires, designated as black wires, play a crucial role in home wiring by transmitting electrical current from the electrical panel to various appliances and devices. While the National Electrical Code (NEC) does not enforce specific color-coding for hot wires, black is widely used for easy identification. It’s important to note that hot wires carry electrical current and must be handled with caution to avoid potential hazards.
Sources:
- Electrical Wire Color Codes: Everything You Need to Know
- Understanding Electrical Wire Color Codes: A Homeowner’s Guide
Importance of Adhering to Color Code Standards
Electrical wiring color codes play a critical role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. Adhering to these standards is essential for electricians, homeowners, and anyone working with electrical wiring.
Key Takeaways:
- Safety: Color codes help identify wires with different functions, preventing incorrect connections and potential hazards.
- Consistency: Standardized colors ensure uniformity in electrical installations, making it easier to troubleshoot and maintain systems.
- Compliance: Color codes follow National Electrical Code (NEC) standards, ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Consequences of Ignoring Color Code Standards:
- Electrical Hazards: Incorrect connections can lead to electrical shorts, fires, or shocks.
- Troubleshooting Difficulties: Without proper color coding, tracing wires for troubleshooting becomes challenging and time-consuming.
- Non-Compliance: Failing to follow color code standards can result in code violations and potential legal consequences.
Proper Application of Color Codes:
- Neutral Wires: White or gray, connected to the silver terminal.
- Ground Wires: Bare copper or green, connected to the green terminal.
- Hot Wires: Black (120V), Red (240V), Blue (ceiling fans), Yellow (multi-way switches), connected to the brass terminal.
Conclusion:
Adhering to color code standards is crucial for the safety, efficiency, and compliance of electrical systems. By following these standards, you can ensure a reliable and hazard-free electrical environment.
Citations:
- Electrical Wiring Color Codes Explained | MTA Electrical Supply
- What Electrical Wire Colors Mean: A Comprehensive Guide | SimpleShowing
Safety Considerations in Home Wiring Color Coding
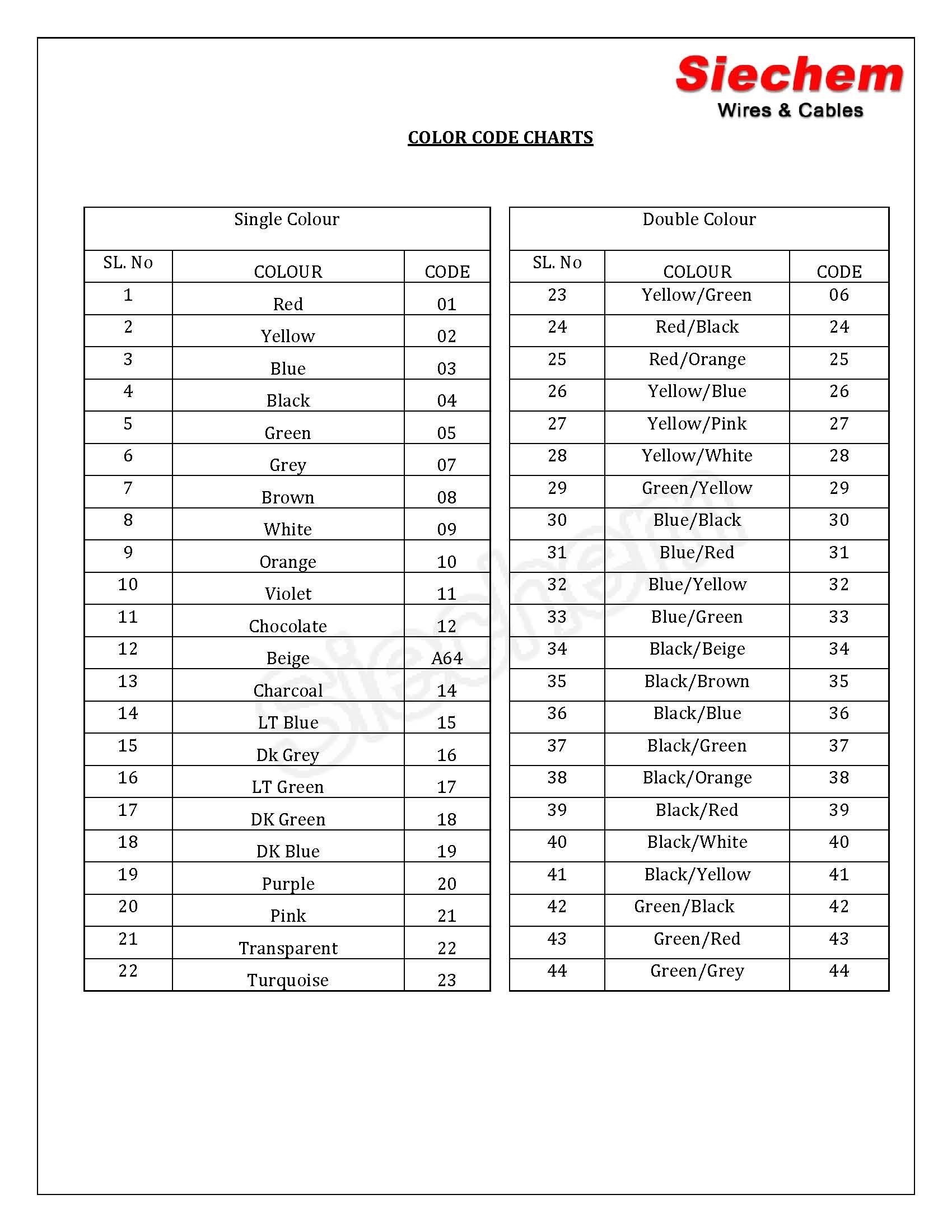
Navigating the intricate world of home wiring demands an astute understanding of color codes for electrical circuits. These color codes serve as a safety beacon, guiding electricians and homeowners alike through the electrical labyrinth of our homes.
Key Takeaways:
- Color coding minimizes the risk of electrical shocks and fire hazards by enabling accurate wire identification.
- Understanding wire color coding ensures compliance with electrical codes and safety regulations.
- Proper color coding facilitates efficient troubleshooting and maintenance, reducing potential hazards.
Understanding Wire Colors
Neutral Wire:
- White or Gray
- Connects to silver screws
Ground Wire:
- Bare Copper or Green
- Connects to green screws
Ground Wire with Yellow Stripe:
- Newer installations for enhanced safety
Hot Wires:
- Black (connects to brass screws)
- Red (typically for 240-volt outlets or wall switches)
- Blue and Yellow (ceiling fans, multi-way switches)
Color-Amperage Relationship:
- White (15 A)
- Yellow (20 A)
- Orange (30 A)
- Black (40 A)
Tips for Safe Wiring Practices:
- Adhere to the National Electrical Code (NEC).
- Choose the correct wire gauge for the amperage requirement.
- Ground circuits properly.
- Label circuits for easy identification.
- Engage a licensed electrician for complex wiring projects.
Conclusion:
Understanding and adhering to home wiring color codes is paramount for ensuring safety and electrical system integrity. By applying these principles, you can navigate the electrical landscape with confidence, safeguarding your home and loved ones from potential hazards.
Sources:
Understanding Electrical Wire Color Codes: A Homeowner’s Guide
Electrical Wire Color Codes Explained | MTA…
FAQ
Q1: What is the purpose of using color codes in home wiring?
Q2: Are there any mandatory wire colors that must be followed according to the National Electrical Code?
Q3: What are the most common colors used for hot wires, neutral wires, and ground wires in home wiring?
Q4: How does proper color coding help in ensuring the safety of electrical installations?
Q5: Why is consistency in wire color coding essential in home wiring?
– Understanding Home Wiring Color Codes for Safe Electrical Work
Embark on an illuminating journey into the world of home wiring color codes with this comprehensive guide. Understanding the nuances of these color standards is paramount for safe and successful electrical work. Whether you’re a seasoned electrician or a DIY enthusiast, this article will empower you with the knowledge to decode the language of your home’s electrical system, ensuring the safety and efficiency of your projects. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of home wiring color codes and unlock the secrets to reliable electrical work: [- Understanding Home Wiring Color Codes for Safe Electrical Work].
Key Takeaways:
- Black is used for hot wires connected to switches.
- Red is for hot wires in 240-volt outlets or wall-controlled switches.
- White or gray indicates neutral conductors.
- Bare copper or green denotes ground wires.
- Ground wires may also have a yellow stripe.
- Blue and yellow are for controlling ceiling fans and three- or four-way switches.
- White or gray must be used for neutral conductors, and bare copper or green for ground wires (per NEC regulations).
- Black, red, and blue are hot wires, representing different phases in a three-phase electrical system.
Home Wiring Color Code
Hey there, home enthusiasts! Let’s unravel the secrets of home wiring color codes. Understanding these codes is essential for safe and effective electrical work.
Why Do Wires Have Colors?
Each color serves a specific purpose, ensuring the safe flow of electricity in your home.
- Black, Red, and Blue: These hot wires carry live current.
- Neutral (White or Gray): This wire completes the circuit, allowing current to return to the source.
- Ground (Green/Green with Yellow, or Bare Copper): This wire protects you from electrical shocks by channeling excess current into the ground.
NEC Mandated Colors
Two colors are strictly regulated by the National Electrical Code (NEC):
- White or Gray: Neutral conductors
- Green or Green with Yellow Stripe: Ground wires
Phase Identification
In homes with 240-volt outlets, hot wires are identified by phase:
- Phase 1: Black
- Phase 2: Red
- Phase 3: Blue
Ceiling Fans and Switches
- Ceiling Fans: Blue and Yellow hot wires indicate different switch speeds.
- Three- and Four-Way Switches: Blue and Yellow hot wires control the light from different locations.
Table of Color Codes
| Wire | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Black | Phase 1 Hot |
| Red | Phase 2 Hot |
| Blue | Phase 3 Hot (240V) |
| White or Gray | Neutral |
| Green or Green with Yellow | Ground |
| Bare Copper | Ground (Rarely used) |
Remember, Safety First!
- Always consult a licensed electrician before performing electrical work.
- Use a multimeter to verify wire colors and voltage before touching any wires.
- If you’re not comfortable working with electricity, it’s best to hire a professional.
-
Are you looking to increase your chances of winning at home? Check out our comprehensive guide on home winning odds to give yourself an edge over the competition.
-
If you’re planning a home renovation project, be sure to consult our detailed home wiring code to ensure a safe and successful installation.
-
Keep your kids engaged and learning at home with our curated collection of home work for class 3 activities.
-
Kickstart your fitness journey with our downloadable home workout plan pdf, designed to help you achieve your fitness goals from the comfort of your own home.
Black, Red, and Blue Wires: Hot Conductors
When dealing with home wiring, understanding the color codes is crucial for both safety and effective electrical work. Knowing which wire is which can help you troubleshoot issues, make repairs, and ensure your electrical system is functioning properly.
Black, Red, and Blue Wires: The Hot Conductors
Among the various wire colors used in home wiring, black, red, and blue stand out as the main conductors carrying live current.
- Black: The primary hot wire, carrying current from the power source to switches, outlets, and other electrical devices.
- Red: A secondary hot wire, typically used for carrying current from a switch to a light fixture, outlet, or other device.
- Blue: A hot wire designated for connecting to light fixtures, especially in three-way or four-way switch configurations.
It’s important to note that the use of blue wires as hot conductors is less common, but you may encounter them in certain lighting or switching scenarios.
Key Takeaways:
- Black wires carry current from the power source.
- Red wires carry current from a switch or other source.
- Blue wires carry current to light fixtures (less common).
- Understanding wire color codes ensures safety and correct wiring.
Sources:
- Mastering Wire Colors: A Complete Guide to Identifying and Organizing Electrical Wires
- Electrical Wire Color Codes: Everything You Need to Know
Green and Bare Wires: Grounding Conductors
Grounding conductors are essential elements of electrical systems, providing a crucial safety measure against electrical shocks. According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), green and bare copper wires are the standard colors for grounding conductors.
Key Takeaways:
- NEC Mandates: Green and bare copper wires are the designated grounding colors.
- Ground Wire Function: Conducts electricity to the ground, preventing shocks.
- Additional Options: Insulated green wires can also serve as grounding conductors.
Safety First: The Importance of Grounding Conductors
Grounding wires provide a vital path for electricity to flow into the earth. This prevents an electrical current from flowing through you if you come into contact with a faulty or live wire. Without proper grounding, electrical shocks and fires can occur.
Making the Connection: Types of Grounding Conductors
- Green or Green with Yellow Stripes: Insulated green wires, either solid or stranded, are the most common type of grounding conductors.
- Bare Copper: Bare copper wires are another acceptable option, especially in industrial or commercial settings.
Ensuring Proper Grounding:
- Always use the designated green or bare copper wires for grounding purposes.
- Securely connect grounding wires to all electrical equipment and outlets.
- Grounding wires should not be used for any other purposes.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can ensure the safety of your electrical system and protect yourself and others from potential electrical hazards.
Sources:
- National Electrical Code (NEC)
- Angi: Electrical Wire Color Codes
Special Cases and Exceptions: Identifying Switch Loops and Travelers
Often, the white wire is reserved for the neutral wire in home wiring, but in switch loops and travelers, the designated wire for the supply is usually white, gray, or bears three continuous white stripes. However, always remember that the NEC (National Electrical Code) requires appropriate wire colors in 3-wire switch loops, replacing the marking of white wires.
Key Takeaways:
- Switch loops and travelers have exceptions to the standard white wire color coding for neutral wires.
- White, gray, or continuously white-striped wires may indicate the supply wire in these scenarios.
- Consult the NEC or a qualified electrician for precise guidelines on switch loop and traveler wire coloring.
Sources:
– 3-Way Switch Wiring Color Code
– Identifying Switch Loops and Travelers – Home Wiring Color Code
FAQ
Q1: What is the purpose of different wire colors in home wiring?
Q2: What are the NEC-mandated colors for ground wires?
Q3: What color wires are used for hot wires in 240-volt outlets?
Q4: Can white wires be used for both neutral and ground connections?
Q5: What is the safety function of a green or bare copper wire in electrical wiring?
- Are Daffodils Perennials?A Complete Guide to Planting & Care - March 31, 2025
- Are Carpenter Bees Dangerous? Stings, Damage, and Control - March 31, 2025
- How to Get Rid of Ants in the Washroom: A Complete Guide - March 31, 2025










