Acceptable Construction Details: Ensuring Structural Integrity and Compliance are vital in the construction industry, especially for external insulation, timber framing, and meeting TGD Part L regulations in 2021.
Key Takeaways:
- ACDs Ensure Compliance: Standardized details meet building regulations on air leakage and thermal bridging.
- Industry Assistance: ACDs guide the construction industry towards meeting performance standards.
Acceptable Construction Details: Ensuring Structural Integrity and Compliance
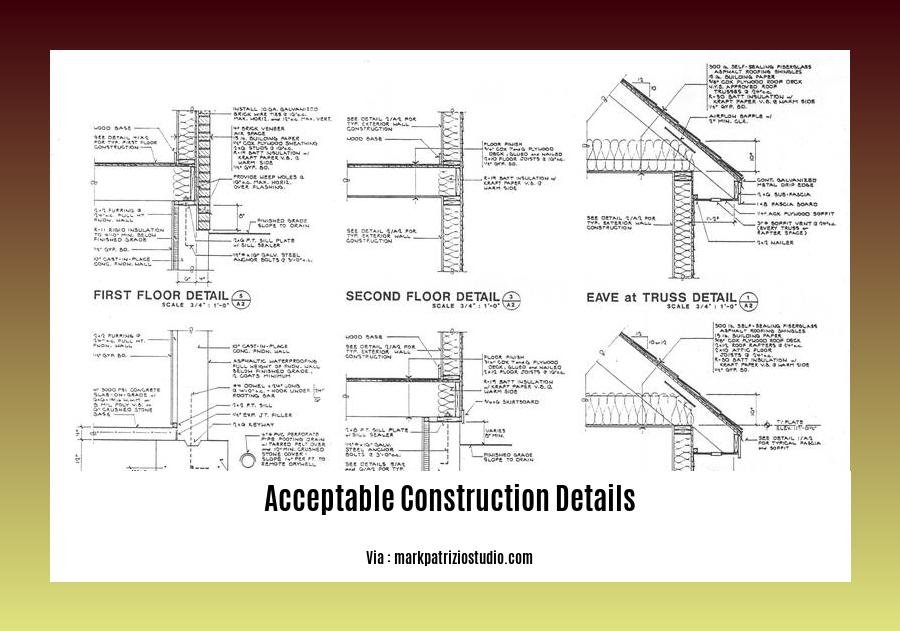
Acceptable construction details (ACDs) are standardized guidelines that demonstrate compliance with building regulations for air leakage and thermal bridging. They guide the construction industry in meeting performance standards outlined in Building Regulations Technical Guidance Document L [1, 2].
Why are ACDs Important?
ACDs provide numerous benefits:
- Ensure code compliance: They help builders adhere to building regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance fines or project delays.
- Improve energy efficiency: ACDs minimize air leakage and thermal bridging, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills.
- Enhance structural integrity: They incorporate best practices for structural stability, ensuring the longevity and safety of buildings.
How to Implement ACDs
Implementing ACDs involves several steps:
- Study the regulations: Familiarize yourself with the Building Regulations Technical Guidance Document L and identify relevant ACDs.
- Select appropriate details: Choose ACDs that meet the specific requirements of the project, considering factors like building type, materials, and climate.
- Incorporate them into designs: Integrate ACDs into construction drawings and specifications to ensure proper implementation.
- Monitor and inspect: Regularly inspect the implementation of ACDs during construction to ensure compliance and identify any deviations.
Benefits of Using ACDs
The benefits of using ACDs extend beyond code compliance and improved energy efficiency:
- Reduced construction defects: By following standardized details, the likelihood of construction defects is minimized.
- Increased building value: Buildings built in compliance with ACDs are more energy-efficient and durable, increasing their value.
- Enhanced reputation: Contractors who demonstrate expertise in implementing ACDs gain a reputation for quality work.
Conclusion
Utilizing ACDs is crucial for ensuring structural integrity, compliance with building regulations, and energy efficiency. By following these standardized guidelines, construction professionals can deliver safe, durable, and cost-effective buildings that meet the demands of modern construction practices.
If you are struggling with the pain after your acl reconstruction, this timeline will give you an idea of what to expect. The cost of a private acl reconstruction can vary depending on a number of factors, so it is important to do your research. Once you have had your acl reconstruction, it is important to follow the recovery exercises carefully to ensure a full recovery. There are also a number of recovery tips that can help you make the process easier. Finally, be sure to follow the rehab exercises prescribed by your doctor to ensure a full and speedy recovery.
TGD Part L Acceptable Construction Details

Key Takeaways:
- TGD Part L Acceptable Construction Details (ACDs) are crucial for achieving thermal continuity and airtightness in building construction.
- ACDs provide detailed guidance on how to prevent heat loss, improve energy efficiency, and comply with building regulations.
- By following ACDs, construction professionals can ensure structural integrity, durability, and occupant comfort.
In today’s construction industry, adhering to TGD Part L Acceptable Construction Details (ACDs) is paramount to delivering high-performance buildings. ACDs play a pivotal role in ensuring structural integrity, energy efficiency, and compliance with building regulations.
Understanding Acceptable Construction Details
ACDs are standardized construction details that provide practical guidance on achieving thermal continuity and airtightness. They outline specific construction methods and materials to minimize heat loss through structural elements and uncontrolled air leakage. By following ACDs, construction professionals can prevent thermal bridging, a major cause of energy inefficiency in buildings.
Types of Acceptable Construction Details
ACDs cover various construction elements, including:
- Masonry walls
- Timber and steel frame walls
- Intermediate floors
- Separating wall junctions
For each element, ACDs provide detailed instructions on:
- Insulation installation and continuity
- Airtightness measures
- Service penetration sealing
- Edge detailing
Benefits of Using Acceptable Construction Details
Implementing ACDs offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced heat loss and improved energy efficiency
- Enhanced occupant comfort and indoor air quality
- Reduced risk of moisture problems and structural damage
- Increased building durability and longevity
- Compliance with building regulations and industry standards
Conclusion
TGD Part L Acceptable Construction Details are essential tools for construction professionals to ensure the delivery of safe, energy-efficient, and durable buildings. By following ACDs, construction companies can demonstrate their commitment to quality, sustainability, and compliance.
Sources:
- Acceptable Construction Details for TGD Part L 2019
- Building Guidelines | Air Leakage | Acceptable Construction Details (ACDs)
Acceptable Construction Details: Timber Frame
Acceptable construction details (ACDs) provide guidance on thermal bridging and airtightness. They aim to help achieve performance standards in Building Regulations Technical Guidance Document L 2021. Timber frame construction allows for various structural forms. Timber frame details include junctions with roofs, ground floors, internal floors, and window openings.
What are the Key Takeaways?
- ACDs are essential for achieving thermal continuity and airtightness in building construction.
- They provide guidance on preventing heat loss and improving energy efficiency.
- ACDs ensure structural integrity, durability, and occupant comfort.
- Proper design and construction of timber frames require input from qualified timber frame contractors and design professionals.
References:
- Technical Guidance Document L – Conservation of Fuel
- Timber Framing Manual – Complete
FAQ
Q1: What are Acceptable Construction Details (ACDs)?
A1: ACDs are standardized construction details that provide guidance on achieving thermal continuity and airtightness in buildings, ensuring compliance with building regulations on air leakage and thermal bridging.
Q2: How do ACDs help achieve performance standards in TGD Part L 2021?
A2: ACDs provide detailed and practical guidance on how to design and construct buildings to meet the thermal continuity and airtightness requirements set forth in the Technical Guidance Document L 2021, which are essential for minimizing heat loss, improving energy efficiency, and enhancing comfort in buildings.
Q3: What are the key considerations for external insulation in ACDs?
A3: ACDs for external insulation focus on providing continuous insulation without thermal bridging, preventing heat loss through structural elements and ensuring the effective performance of insulation materials.
Q4: How do ACDs address thermal continuity and airtightness in timber frame construction?
A4: ACDs for timber frame construction provide specific guidance on junctions between roofs, ground floors, internal floors, and window openings, ensuring proper sealing and preventing air leakage or thermal bridging.
Q5: How do ACDs promote structural integrity in construction?
A5: By ensuring thermal continuity and airtightness, ACDs contribute to the overall structural integrity of buildings by preventing moisture penetration, reducing thermal stress on building elements, and minimizing the risk of condensation and related structural damage.
- Greenhouse Storage Shed Combos: Your Guide to Combining Growing and Storage - April 21, 2025
- Greenhouse Shed Combo: Design, Build & Grow Year-Round - April 21, 2025
- Gingham vs. Plaid: What’s the Difference? A Complete Guide - April 21, 2025










