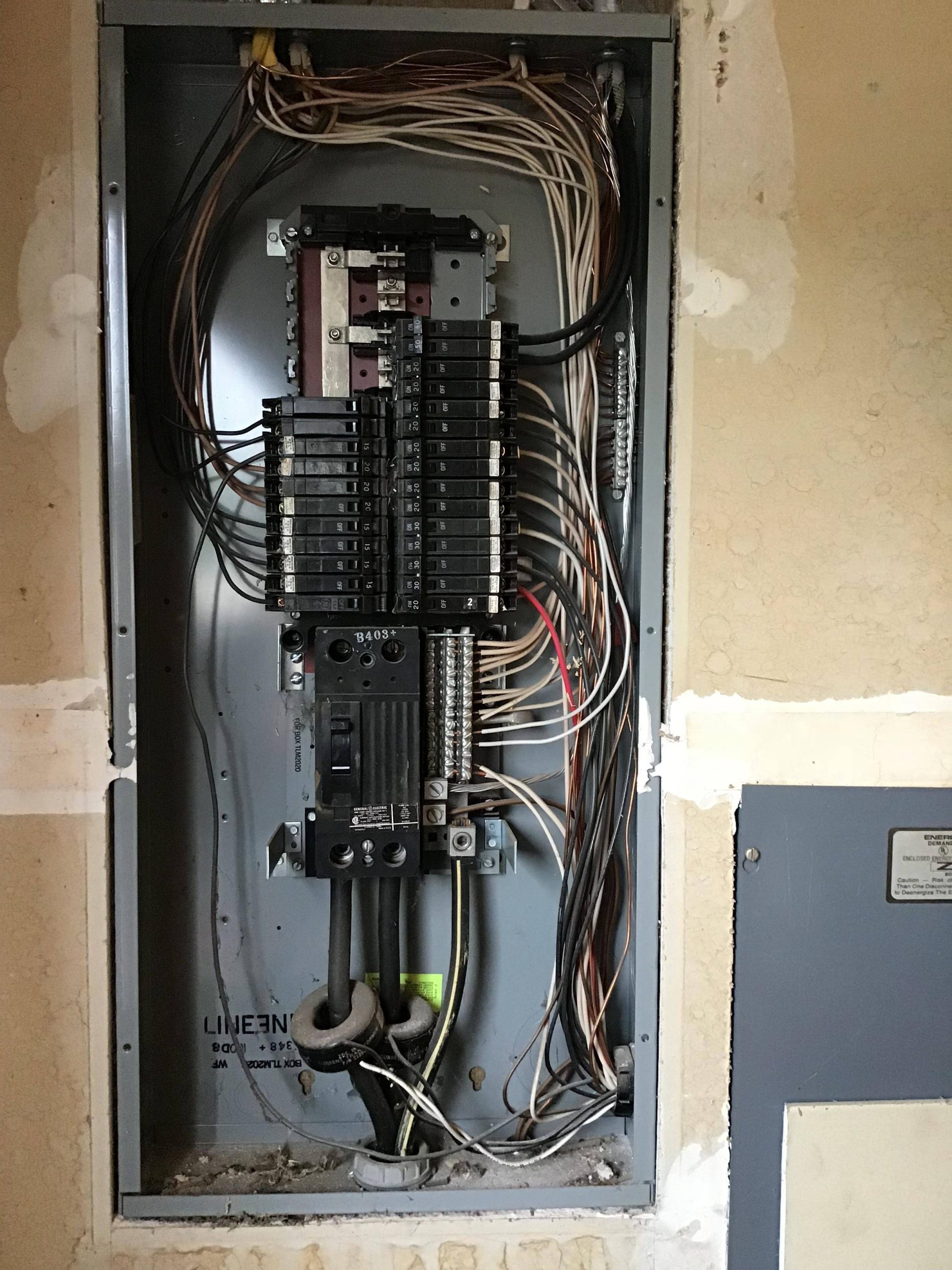
Ever wonder about that unassuming gray metal box tucked away in your basement or garage? It’s your electrical panel, the heart of your home’s power system, and understanding it can enhance your safety and help you troubleshoot common electrical issues. This guide breaks down the essentials, from identifying potential problems to understanding the key components within. No need for an electrician’s license – we’ll keep it simple and straightforward.
What’s Inside That Box?
Your electrical panel, also known as a breaker box, service panel, load center, or distribution board, is the central hub for all electricity flowing through your house. It receives power from the utility company and distributes it to various circuits, powering everything from lights and appliances to bottom strip of walls outlets. This carefully organized system not only distributes power but also acts as a crucial safety device, preventing overloads and protecting your electrical system from damage.
Decoding Your Home’s Electrical Distribution Center
This metal enclosure isn’t just a container; it’s a sophisticated system that divides the incoming power into dedicated circuits for specific areas or appliances. This division ensures that an overload in one area doesn’t affect the entire house. The panel’s safety mechanisms, primarily the circuit breakers, protect your electrical system from damage by automatically shutting off power in case of a fault.
Warning Signs: When to Call a Pro
A well-maintained electrical panel is paramount for safety. Older panels, particularly Federal Pacific Electric (FPE) Stab-Lok and Zinsco panels, are now considered potential fire hazards due to their design and age. If you have one of these older panels, consulting a licensed electrician for inspection and potential replacement is highly recommended. Some experts believe these panels may malfunction and pose a safety risk.
Beyond panel age, other warning signs suggest a potential problem. Frequently tripping breakers, burning smells near the panel, and flickering lights could indicate issues within your electrical panel. Addressing these promptly can prevent more serious problems down the line.
Key Components and Their Functions
Let’s explore the inner workings of your electrical panel (figuratively, of course – leave the actual exploration to a qualified electrician!). Inside, several key components work together to manage and protect your home’s electrical flow:
- Main Breaker: This master switch controls all power to the panel. It trips during major overloads or short circuits, cutting off power and safeguarding your home.
- Branch Circuit Breakers: These smaller breakers protect individual circuits. They trip if their designated circuit is overloaded, preventing overheating and potential fires.
- Neutral Bus Bar: This acts as the return path for electricity, completing the electrical circuit after power flows through appliances and lights.
- Ground Bus Bar: This critical safety component provides a path for excess current to flow safely to the ground in case of a fault, protecting you from electrical shocks.
These components work in concert to ensure your electrical system operates safely and efficiently.
Modern Panels: Safety and Smart Features
Modern electrical panels offer substantial improvements over their older counterparts. If you’re considering an upgrade, here’s what you can expect:
- Increased Capacity: Modern panels handle higher power demands, accommodating the increasing load from modern appliances and electronics, including electric vehicle charging stations.
- Enhanced Safety: Features like Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) detect dangerous arcing, and Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) protect against shocks in wet areas.
- Smart Home Integration: Some panels offer smart home capabilities, allowing remote control and monitoring of your electrical system via smartphone or tablet.
- Long-Term Savings: While the upfront cost is higher, modern panels can lead to long-term cost savings through increased energy efficiency and reduced risk of electrical problems.
Panel Maintenance and Safety
While DIY repairs are strongly discouraged, regular visual inspections of your panel for damage, loose connections, or overheating are recommended. Ensure the area around your panel is clear and well-ventilated to prevent heat buildup. For any significant electrical work, always consult a licensed electrician.
Different Types of Electrical Boxes
While the electrical panel is a central player, other electrical boxes also contribute to your home’s electrical system. Understanding these different types is essential:
Junction Boxes: The Silent Guardians
Junction boxes, often called j-boxes, house wire connections within walls and ceilings. They protect these connections from damage, moisture, and pests, preventing short circuits and ensuring safe, continuous electrical flow. Junction boxes come in various materials like metal and plastic, offering varying degrees of durability and protection.
Outlet Boxes and Specialized Enclosures
Outlet boxes, ceiling boxes, and device boxes house specific electrical components like receptacles, switches, light fixtures, and ceiling fans. These specialized enclosures provide secure housing, anchor the devices, and maintain organization within the electrical system. They come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different components.
Choosing the Right Box
Selecting the correct electrical box depends on several factors, including location, the number and size of wires, and the type of device it will house. An improperly sized box can lead to overcrowding, creating a fire hazard. The box’s material also plays a role – metal offers durability while plastic provides a lighter, corrosion-resistant alternative.
Safety First: Professional Expertise
While simple tasks like replacing an outlet cover might be manageable for DIYers, complex electrical work should always be left to qualified electricians. They possess the knowledge and tools to handle electrical projects safely and effectively, ensuring your home’s electrical system is up to code and operating correctly. Ongoing research continues to enhance electrical safety practices, so consulting a professional ensures you’re up-to-date with the latest recommendations. Discover the surprising effects of using boiling water PVC pipe for related plumbing projects.
This comprehensive guide should empower you with a better understanding of your home’s electrical system, enabling safer practices and informed decision-making. Remember, electricity deserves respect, so always prioritize safety and seek professional help when needed.
- How to Get a Free Mold Inspection (and Avoid the Scams) - April 23, 2025
- How to Flush a Toilet Without Water: A Step-by-Step Guide - April 23, 2025
- The Complete Guide to Safely Disposing of Light Globes - April 23, 2025