Delve into the realm of sustainable electronic waste management with our comprehensive guide, [- Mastering E-Waste Management Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide to Sustainable Disposal and Recycling]. Embark on a journey to understand the significance of responsible e-waste disposal, the latest techniques and best practices for recycling, and the impact of circular economy models in minimizing electronic waste’s environmental footprint.
Key Takeaways:
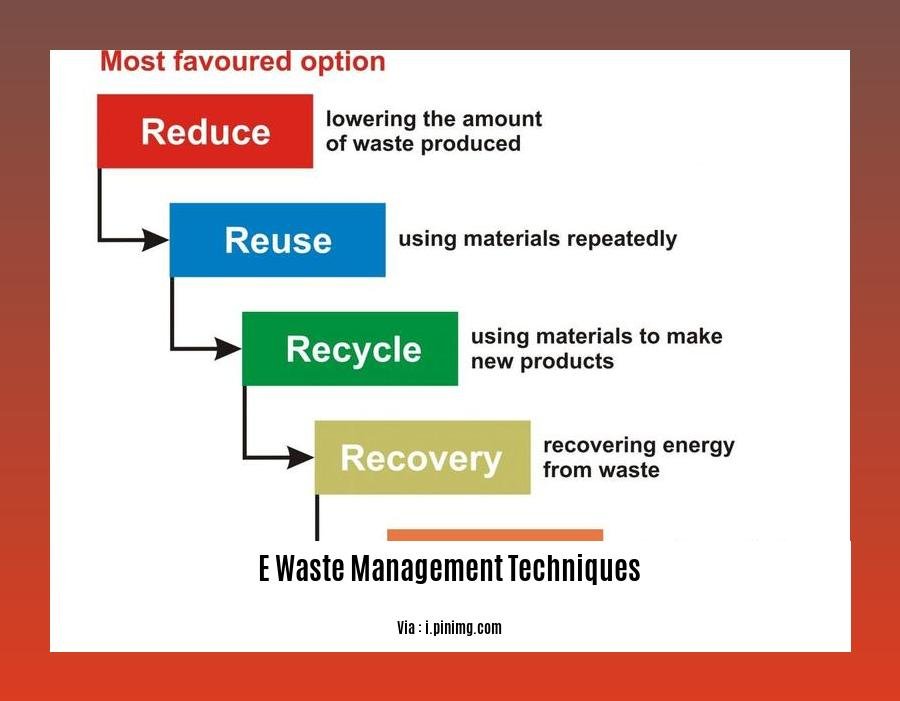
- E-waste management techniques aim to reduce the harmful impact of electronic waste on the environment.
- Landfilling, recycling, incineration, and strict regulation are common methods used to manage e-waste.
- Landfilling can lead to the release of toxic substances into the environment, contaminating soil and groundwater.
- Recycling recovers valuable materials from e-waste, minimizing its environmental impact.
- Incineration releases harmful pollutants into the air, making it an undesirable method.
- Strict regulations control the disposal of e-waste, ensuring proper waste management practices.
E-waste Management Techniques

In this digital age, electronic devices have become an indispensable part of our lives. However, as technology advances, so does the amount of electronic waste (e-waste) we generate. E-waste is a growing problem, and it’s essential to adopt effective e-waste management techniques to protect our environment and health.
Step-by-Step Guide to E-waste Management
- Identify and Segregate E-waste:
- Identify electronic devices that are no longer in use, damaged, or obsolete.
-
Segregate e-waste from other types of waste, such as household garbage or recyclables.
-
Proper Packaging and Storage:
- Ensure e-waste items are appropriately packaged to prevent damage during transportation.
-
Store e-waste in a designated area until it can be collected for recycling or disposal.
-
Explore Recycling Options:
- Research local recycling facilities that accept e-waste.
- Choose reputable recycling companies certified in responsible e-waste handling.
-
Ensure the recycler follows proper procedures to extract valuable materials and dispose of hazardous components safely.
-
Safe Disposal of Hazardous E-waste:
- Certain e-waste items, such as batteries, contain hazardous materials requiring special handling.
-
Contact your local hazardous waste disposal facility for guidance on proper disposal methods.
-
Educate and Raise Awareness:
- Educate yourself and others about the importance of proper e-waste management techniques.
-
Share information about e-waste recycling programs and encourage responsible disposal.
-
Support Sustainable Product Design:
- Choose electronic products designed with sustainability in mind.
-
Look for products made from recycled materials and designed for easy disassembly and recycling.
-
Regularly Update Electronic Devices:
-
Keep your electronic devices updated with software patches and security fixes to extend their lifespan.
-
Safe Disposal of Sensitive Data:
- Before discarding electronic devices, ensure you have backed up and erased all sensitive data to protect your privacy.
Conclusion
By adopting responsible e-waste management techniques, we can collectively reduce the environmental impact of electronic waste, conserve natural resources, and promote a sustainable future for generations to come.
-
Looking to get in touch with Coventry Homefinder? Their contact number is just a click away! Coventry Homefinder contact number
-
Need to reach Coventry Homefinder? Find their phone number here with just a click! Coventry Homefinder phone number
-
Unleash your creativity and explore the beauty of your favorite festival in Hindi. Read this essay to immerse yourself in the vibrant colors and traditions! Essay on my favourite festival in Hindi
-
Discover the fascinating facts about Odisha, a land of rich history, diverse culture, and natural wonders. Facts about Odisha
Encouraging Responsible Manufacturing Practices
Hello there! Are you aware of the growing e-waste crisis and its profound impact on our environment? Electronic devices have become an integral part of our lives, but discarding them irresponsibly can lead to severe consequences. That’s where responsible manufacturing practices come into play.
Let’s dive into some crucial steps manufacturers can take to minimize e-waste and promote a circular economy:
1. Design for Durability and Longevity:
– Prioritize durable materials and construction methods to increase the lifespan of electronic devices.
– Offer repair and upgrade services to extend product life cycles.
– Provide clear instructions for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
2. Incorporate Recycled Materials:
– Use recycled materials in the manufacturing process to reduce the demand for virgin resources and minimize waste.
– Explore innovative ways to incorporate recycled e-waste components into new products.
3. Design for Easy Recycling:
– Ensure products are designed for easy disassembly and recycling.
– Use standardized components and materials to facilitate recycling processes.
– Provide clear recycling instructions and support programs for consumers.
4. Take Back and Recycling Programs:
– Implement take-back programs where consumers can return end-of-life electronic devices to manufacturers for proper recycling.
– Partner with recycling facilities to ensure proper e-waste disposal and resource recovery.
5. Collaborate for Sustainable Solutions:
– Collaborate with other manufacturers, industry associations, and government agencies to develop and implement sustainable manufacturing standards.
– Share best practices and innovative technologies to improve the collective environmental performance of the industry.
Key Takeaways:
-
Responsible manufacturing practices are crucial for reducing e-waste and promoting a circular economy.
-
Manufacturers can contribute to reducing e-waste by designing products for durability, longevity, and easy recycling.
-
Implementing take-back and recycling programs, using recycled materials, and collaborating with stakeholders are key steps toward sustainable manufacturing.
-
By adopting responsible practices, manufacturers can minimize their environmental impact and contribute to a greener future.
Remember, every step towards responsible manufacturing is a step towards a sustainable future. Let’s work together to minimize e-waste and create a circular economy where electronic devices are used, reused, and recycled responsibly.
Sources:
Sustainable Manufacturing Strategies for Reducing E-Waste
EPR: A Key to Sustainable E-waste Management
Raising Awareness and Education: A Collective Responsibility
Hey there! In the pursuit of combating the e-waste crisis, let’s band together to elevate awareness and foster education. It’s not just about knowing what to do with old electronics; it’s about transforming our collective behavior and inspiring others to do the same. Imagine a future where every individual understands the grave consequences of improper e-waste disposal and actively participates in sustainable recycling and disposal practices. That’s the world we’re striving for!
Key Takeaways:
-
Educate Yourself: Embark on a journey of continuous learning about electronic waste and its multifaceted impact on our planet. Understand the risks posed by hazardous materials found in e-waste and delve into responsible disposal methods, recycling initiatives, and eco-friendly alternatives.
-
Spread the Word: Become an ambassador of change by sharing your knowledge with friends, family, neighbors, and colleagues. Engage in conversations about e-waste, sparking curiosity and inspiring others to adopt sustainable practices. Leverage social media platforms to amplify your message and reach a broader audience.
-
Engage Schools and Communities: Collaborate with local schools, universities, and community centers to incorporate e-waste awareness into educational programs. Develop engaging workshops, seminars, and interactive activities that teach students and community members about the importance of responsible e-waste management.
-
Empower Businesses and Organizations: Encourage businesses and organizations to prioritize e-waste management as part of their environmental responsibility. Provide guidance on implementing e-waste recycling programs, conducting regular audits, and educating employees about sustainable practices.
-
Advocate for Policy Change: Join forces with like-minded individuals and organizations to advocate for policies that support and incentivize responsible e-waste management. Participate in public forums, submit comments to regulatory agencies, and engage with elected officials to advocate for stronger regulations and initiatives.
We’re All in This Together
Remember, change doesn’t happen overnight. It requires a concerted effort, one step at a time. As you educate yourself and others, you’re creating a ripple effect that has the power to transform how we view and manage electronic waste. Together, we can create a sustainable future where e-waste is no longer a threat to our planet. Let’s be part of the solution!
Sources:
- The Role of Education in Promoting Responsible E-Waste Management
- E-Waste Management: A Growing Concern
Implementing Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Programs
Have you ever wondered where your old electronic devices end up once you’re done with them? Unfortunately, many of these devices end up in landfills or are illegally dumped, posing significant environmental and health hazards. That’s where Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs come in – a game-changing approach to tackling the growing e-waste crisis.
Key Takeaways:
- Producer Responsibility: EPR shifts the burden of e-waste management from municipalities and consumers to producers, incentivizing them to design products that are easier to recycle and reuse.
- Design for Sustainability: EPR encourages eco-friendly product design, using recyclable materials, and employing modular components for easier repairs, extending product lifespans.
- Take-back and Recycling Systems: Producers are responsible for setting up collection and recycling systems, making it convenient for consumers to return their old devices for proper recycling or refurbishing.
- Financial Incentives: EPR programs often involve financial incentives for consumers, such as discounts on new products or recycling rewards, to encourage responsible e-waste disposal.
- Regulatory Framework: Governments play a crucial role in implementing and enforcing EPR regulations, ensuring that producers comply with their responsibilities.
Steps for Implementing EPR Programs:
-
Stakeholder Engagement: Engage all relevant stakeholders, including producers, retailers, waste management companies, and consumers, to gather input and support.
-
Legislative Framework: Develop a comprehensive legal framework that outlines the roles and responsibilities of producers, collection systems, and recycling facilities.
-
Product Registration and Labeling: Establish a system for producers to register their products and affix labels indicating the product’s recyclability and end-of-life disposal options.
-
Collection and Recycling Infrastructure: Set up convenient collection points and recycling facilities to ensure easy access for consumers to dispose of their e-waste responsibly.
-
Producer Financing: Implement mechanisms for producers to contribute financially to the cost of e-waste management, including collection, recycling, and awareness campaigns.
-
Enforcement and Monitoring: Establish a system for monitoring producer compliance and enforcing regulations, ensuring that producers fulfill their responsibilities effectively.
Benefits of EPR Programs:
-
Reduced Environmental Impact: EPR programs help reduce the amount of e-waste going to landfills and incinerators, minimizing the release of toxic chemicals into the environment.
-
Increased Recycling and Material Recovery: EPR incentivizes producers to design products that are easier to recycle, leading to higher recycling rates and the recovery of valuable materials.
-
Promote Circular Economy: EPR supports the circular economy model, where products and materials are kept in use for as long as possible, reducing the need for raw material extraction and minimizing waste.
-
Economic Opportunities: EPR programs can create new business opportunities in recycling and waste management, leading to job creation and economic growth.
Challenges of EPR Programs:
-
Complexity of Implementation: EPR programs can be complex to implement, requiring collaboration among various stakeholders and the development of robust regulatory frameworks.
-
Cost Implications: The cost of implementing and operating EPR programs can be significant, requiring financial contributions from producers and potentially leading to higher prices for consumers.
-
Lack of Consumer Awareness: Raising consumer awareness about EPR programs and responsible e-waste disposal practices is essential for the success of these programs.
-
Cross-border Challenges: In a globalized economy, addressing e-waste requires international cooperation and harmonized regulations to ensure consistent implementation and prevent illegal transboundary shipments of e-waste.
Conclusion:
EPR programs are critical for addressing the growing e-waste crisis and promoting sustainable waste management practices. By shifting the responsibility to producers, incentivizing eco-friendly product design, and establishing collection and recycling systems, EPR programs can effectively reduce the environmental impact of electronic devices and foster a more circular economy. Overcoming the challenges and ensuring the successful implementation of EPR programs requires collaboration, innovation, and a shared commitment to a sustainable future.
References:
- Implementing Extended Producer Responsibility for E-waste
- E-waste Management: A Case Study of Extended Producer Responsibility
FAQ
Q1: What are the primary techniques for managing e-waste?
A1: E-waste management involves various techniques such as landfilling, recycling, incineration, and strict regulation. Landfilling involves burying e-waste, potentially leading to environmental contamination. Recycling is crucial for recovering valuable materials while minimizing environmental impact. Incineration releases harmful pollutants into the air and is generally undesirable. Strict regulation helps control the impact of e-waste and ensures proper waste management practices.
Q2: How does Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) contribute to effective e-waste management?
A2: Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) holds producers responsible for the entire life cycle of their products, including end-of-life disposal and recycling. EPR programs encourage producers to use eco-friendly materials, design products for easy recycling, and establish collection and recycling systems. By shifting the responsibility upstream, EPR incentivizes sustainable product design and minimizes the burden on waste management systems.
Q3: What role does technology innovation play in enhancing e-waste management?
A3: Technological innovation offers promising solutions for improving e-waste management. Developing innovative recycling technologies enhances the efficiency and profitability of e-waste recycling, leading to higher recovery rates of valuable materials. Additionally, implementing e-waste tracking systems enables tracking the movement of electronic waste, ensuring proper disposal and recycling, and facilitating accountability in the e-waste management chain.
Q4: How can public awareness and education contribute to effective e-waste management?
A4: Public awareness and education are crucial in promoting responsible e-waste disposal. Campaigns and initiatives aimed at informing individuals and communities about the environmental and health impacts of improper e-waste disposal can significantly influence waste management behaviors. Educating consumers about available disposal options, such as designated e-waste recycling centers, encourages proper waste disposal practices and reduces the amount of e-waste ending up in landfills or being illegally dumped.
Q5: What is the significance of global cooperation and policy advocacy in addressing e-waste management challenges?
A5: Global cooperation and policy advocacy are essential in tackling the global challenge of e-waste. Establishing international standards, guidelines, and regulations for e-waste management fosters responsible practices across countries. Collaboration among governments, industries, and environmental organizations enables the sharing of best practices, facilitates technology transfer, and promotes harmonized approaches to e-waste management. Policy advocacy at the national and international levels helps drive supportive policies that promote e-waste recycling, minimize the production of hazardous e-waste, and encourage sustainable waste management practices.
- Finishes For Butcher Block Counters: Choosing The Right Food-Safe Option - December 28, 2025
- Kitchen Countertop Ideas: Find the Perfect Surface for You - December 27, 2025
- Stove Backsplash Design: Ideas to Elevate Your Kitchen Style - December 26, 2025










