– A Comprehensive Guide to the Rural Road Construction Process: Planning, Design, and Implementation –
Key Takeaways:
- Planning and Design:
- Outline project goals, secure funding, and conduct initial engineering studies.
- Demolition and Clearing:
- Remove any existing structures and vegetation.
- Ground Works:
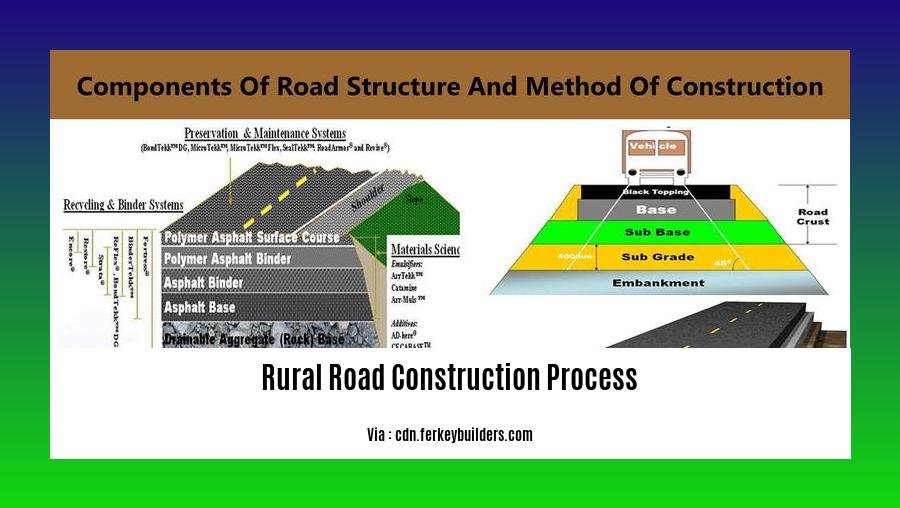
- Prepare the land by excavating, grading, and compacting the subgrade.
- Sub-Base Construction:
- Install a stable layer of crushed stone or gravel.
- Binder Application:
- Apply a layer of asphalt binder to the sub-base.
- Asphalt Paving:
- Install the final surface layer of asphalt.
Rural Road Construction Process

Greetings, engineers! Buckle up for a deep dive into the intricacies of rural road construction – an indispensable skill for shaping the infrastructure of remote communities.
Step 1: Planning and Design
Lay the groundwork with a meticulous plan and design. This entails understanding the project’s scope, securing funds, and meticulously evaluating the terrain. Rural roads demand a keen eye for topography, environmental impact, and community needs.
Step 2: Demolition and Clearing
Clear the path for progress! Remove existing obstacles like structures and vegetation to make way for the new road. Handle this with care, minimizing environmental disruption and respecting cultural heritage.
Step 3: Ground Works
Dig it, grade it, and compact it! Prepare the subgrade – the foundation of your road – through excavation, grading, and compaction. Ensuring a stable base is crucial for a road that stands the test of time.
Step 4: Sub-Base Construction
Provide stability with a layer of crushed stone or gravel. This sub-base acts as a shock absorber, distributing loads and preventing ground movement from damaging the road.
Step 5: Binder Application
Time for the glue! Apply a layer of asphalt binder to the sub-base. Think of it as the adhesive that holds everything together, ensuring a smooth and durable surface.
Step 6: Asphalt Laying
The final touch – lay the asphalt! Apply the top layer of asphalt, the surface that vehicles will travel on. Precision is key here, ensuring the road is level, well-compacted, and ready to handle the rigors of traffic.
Additional Tips for Rural Road Construction
- Embrace sustainability: Opt for environmentally friendly materials and construction techniques to minimize ecological impact.
- Engage with the community: Seek input and address concerns from local residents, building trust and ensuring community buy-in.
- Monitor and maintain: Regular inspections and timely repairs are essential for keeping rural roads in prime condition.
Get the best tools and construction equipment from our extensive road construction machinery list to help you with your construction work.
Learn more about the important roles and responsibilities of a safety officer in construction to ensure a safe and hazard-free job site.
Materials Selection and Procurement

When embarking on rural road construction, materials selection and procurement play a critical role in ensuring the project’s success. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate this crucial aspect:
Key Takeaways:
- Materials selection aligns with road specifications: Determine the road’s intended use, traffic volume, and environmental conditions to select appropriate materials.
- Responsible sourcing considers sustainability: Choose materials that minimize environmental impact and promote social welfare.
- Budgetary considerations: Balance the cost of materials with project goals and constraints.
- Specific equipment and materials: Road construction requires specialized equipment like compactors, motor graders, and asphalt plants.
Material Selection
- Evaluate project requirements: Determine the specific qualities needed for the sub-base, binder, and surface layers.
- Research material options: Explore different materials, such as asphalt, concrete, gravel, and recycled materials.
- Consider environmental factors: Analyze the impact of materials on the surrounding ecosystem.
- Select durable and cost-effective materials: Choose materials that can withstand the anticipated traffic and environmental conditions, within the project’s budget.
Material Procurement
- Identify reliable suppliers: Establish relationships with reputable suppliers who can provide quality materials on time.
- Secure contracts: Negotiate contracts that clearly define material specifications, quantities, and delivery schedules.
- Monitor deliveries: Track the progress of material deliveries to ensure they meet project deadlines.
- Inspect materials: Inspect materials upon arrival to verify they meet the agreed-upon specifications.
Conclusion
Responsible materials selection and procurement are essential for creating safe, durable, and environmentally friendly rural roads. By following these guidelines, you can ensure the project’s success and contribute to the sustainable development of rural communities.
Relevant URL Sources:
- Strategic Approach to the Selection and Procurement of Construction Materials
- Road Construction Using Locally Available Materials
Construction and project management
Effective Construction and project management is crucial for the success of rural road construction. Let’s delve into the key practices:
Stakeholder Management
Engage with community members, government agencies, landowners, and contractors to ensure their perspectives are considered. Open communication and proactive conflict resolution are key.
Proper Planning
Define clear project objectives, conduct thorough site surveys, establish accurate cost estimates, and create realistic timelines. Detailed planning avoids costly delays and rework.
Cost Management
Track expenses diligently, optimize resource allocation, and implement cost-control measures. Prevent budget overruns by adhering to procurement policies and negotiating favorable contracts.
Quality Control
Establish clear construction standards and specifications. Regularly inspect materials, workmanship, and progress to ensure adherence to quality norms. This prevents safety hazards and premature road deterioration.
Key Takeaways:
- Stakeholder management aligns project goals with community needs.
- Proper planning sets a solid foundation for efficient construction.
- Cost management optimizes resource allocation and prevents budget overruns.
- Quality control ensures road safety and longevity.
Relevant URL Sources:
- Project Management and Performance of Rural Road Construction Projects in Machakos County, Kenya
- Stakeholder Management in Rural Road Construction Projects
Maintenance and sustainability
Now that we’ve covered the basics of rural road construction, let’s shift our focus to the important topic of maintenance and sustainability. After all, once a road is built, it’s crucial to maintain its quality and longevity while minimizing its environmental impact.
Step 1: Regular Inspections
Just like your car, rural roads need regular checkups to identify any potential issues. Inspections should focus on:
- Surface damage: Cracks, potholes, or uneven surfaces
- Drainage: Ensure water is flowing properly to prevent washouts
- Signage and markings: Legibility, visibility, and compliance with regulations
- Vegetation: Overgrowth can obstruct visibility and damage pavement
Step 2: Timely Repairs
Once issues are identified, prompt repairs are essential. This not only prolongs the road’s life but also prevents minor problems from turning into major hazards.
Step 3: Sustainable Materials
When making repairs or resurfacing, consider using sustainable materials such as:
- Recycled asphalt: Reduces waste and conserves resources
- Permeable pavements: Allow rainwater to infiltrate the ground, reducing runoff and erosion
Step 4: Green Infrastructure
Incorporate green infrastructure into your maintenance practices, such as:
- Bioswales: Vegetated channels that filter stormwater runoff
- Rain gardens: Depressions that capture and soak up rainwater
Key Takeaways:
- Regular inspections and timely repairs extend the life of rural roads.
- Sustainable materials and green infrastructure minimize environmental impact.
- Maintaining rural roads safely and efficiently supports rural development and community well-being.
Citations:
- World Bank: Rural Road Maintenance and Improvement
- Springer: Sustainability of Rural Roads
FAQ
Q1: What are the key steps involved in the planning and design phase of rural road construction?
Q2: How does material selection impact the sustainability and durability of rural roads?
Q3: What project management practices are crucial for the successful implementation of rural road projects?
Q4: How can rural road construction minimize environmental impacts while meeting the needs of local communities?
Q5: What innovative techniques are being used to enhance the safety and efficiency of rural road projects?
- Kitchen tiling wall: Elevate your kitchen with stylish wall tiles - December 16, 2025
- Gray Kitchen Backsplash Tile: Ideas for a Stylish Upgrade - December 14, 2025
- Backsplash For Gray Cabinets: Choosing the Right Backsplash Style - December 13, 2025