Delve into the realm of construction technology with our comprehensive guide on BBM (Building Information Modeling) in construction, aptly titled “[Title: BBM Full Form in Construction: Building Information Modeling (BIM) Explained]”. Discover the intricacies of BIM, its transformative role in the industry, and practical insights into its implementation, benefits, and challenges. Get ready to unravel the secrets of this groundbreaking technology that is revolutionizing the way we design, build, and manage structures.
Key Takeaways:
- BBM is commonly referred to as Building Information Modeling (BIM) in the construction industry.
- BIM involves creating a virtual representation of a building for planning, design, and construction.
- BIM can streamline communication among project stakeholders, improving efficiency and coordination.
- BIM facilitates clash detection, cost estimation, and time management, reducing errors and delays.
- BIM supports sustainable design and allows for better facility management throughout the building’s lifecycle.
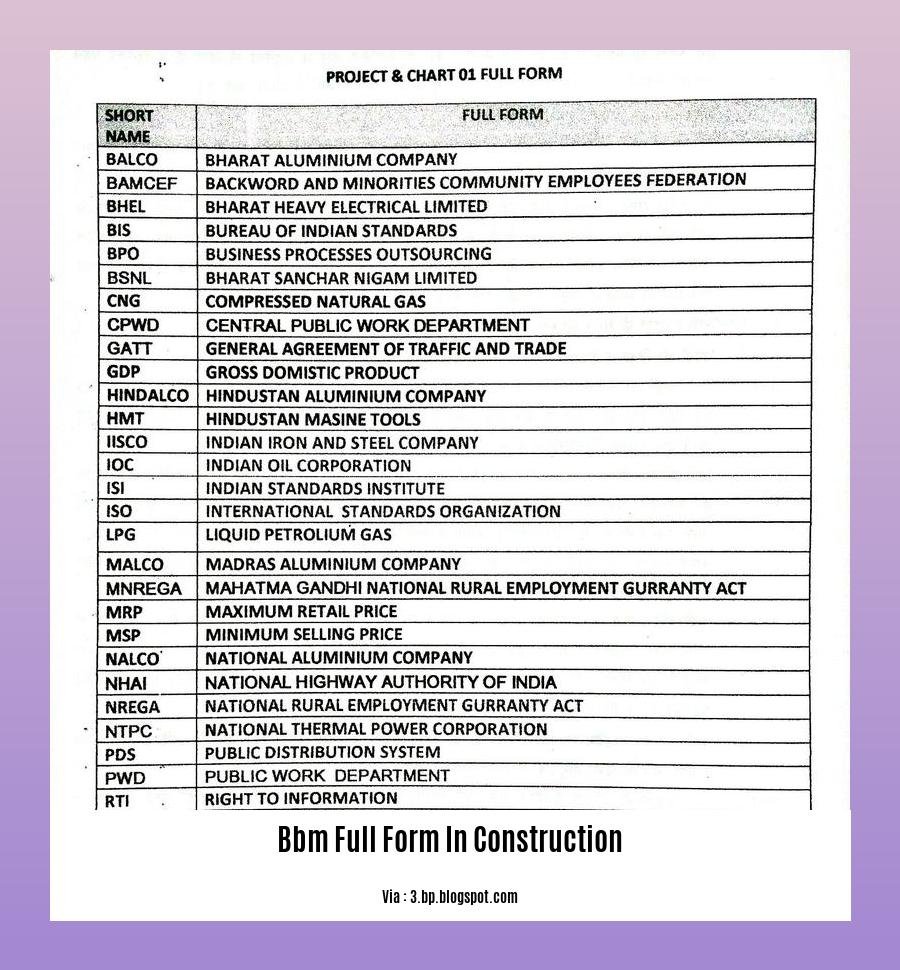
BBM Full Form in Construction

BBM within the construction industry can refer to the following terms:
- Bitumen Bound Macadam (BBM): A construction material used for road surfaces, consisting of crushed stone or gravel bound together with bitumen.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): A digital representation of a building or facility that encompasses physical and functional characteristics.
Bitumen Bound Macadam (BBM)
Benefits of BBM:
- Rapid construction
- Cost-effectiveness
- Durable and resistant to wear and tear
Applications of BBM:
- Road surfaces
- Parking lots
- Driveways
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Benefits of BIM:
- Improved collaboration and communication among project stakeholders
- Enhanced design coordination
- Reduced construction errors and rework
- Increased project efficiency and productivity
Applications of BIM:
- Architectural design
- Structural engineering
- Mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems
- Construction management
- Facility management
Key Advantages of BIM in Construction:
- Improved decision-making: BIM provides a centralized platform for project stakeholders to access and collaborate on project information, enabling better decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
- Reduced design conflicts: BIM allows for early identification and resolution of design clashes, minimizing the risk of costly errors and delays.
- Increased productivity: BIM streamlines the construction process, reducing rework and improving efficiency.
- Enhanced collaboration: BIM facilitates seamless collaboration among project teams, reducing communication barriers and improving teamwork.
· Do you want to know about 5 Marla House Construction Cost in Pakistan 2023? Click here.
· For detailed information about Balcony Construction Details, click here.
· Interested in Basic Construction Company? Click here to know more.
· You can click here for all the Basic Concepts in Construction Productivity Enhancement.
· Click here for more data about BBS Meaning in Construction.
· Don’t miss out on Beam in Construction Meaning; click here to learn more.
BIM Implementation: Planning, Workflow Optimization, and Stakeholder Involvement
BIM implementation is a complex undertaking that requires careful planning, workflow optimization, and stakeholder involvement. By following these best practices, you can ensure a successful BIM implementation that will benefit your project.
Planning
- Define your goals and objectives for BIM implementation.
- Identify the stakeholders who will be involved in the BIM process.
- Develop a BIM execution plan that outlines the roles and responsibilities of each stakeholder.
- Create a BIM model that is tailored to your project’s specific needs.
- Implement a change management process to track and manage changes to the BIM model.
Workflow Optimization
- Establish clear communication channels for BIM coordination.
- Use BIM software to automate tasks and streamline workflows.
- Develop templates and standards to ensure consistency in BIM modeling.
- Train stakeholders on BIM software and best practices.
- Monitor and evaluate BIM implementation to identify areas for improvement.
Stakeholder Involvement
- Engage stakeholders early in the BIM implementation process.
- Establish a stakeholder management plan that outlines the roles and responsibilities of each stakeholder.
- Hold regular stakeholder meetings to review progress and address issues.
- Get feedback from stakeholders on the BIM model to ensure that it meets their needs.
- Use BIM to facilitate collaboration and decision-making among stakeholders.
Key Takeaways:
- BIM implementation requires careful planning, workflow optimization, and stakeholder involvement.
- By following best practices, you can ensure a successful BIM implementation.
- BIM can improve collaboration, reduce errors, and increase efficiency in construction projects.
Relevant URL Sources:
- BIM Implementation: A Guide to Building Information Modeling for Project Management
- BIM Implementation in Construction Projects: A Practical Guide
Challenges and Limitations of BIM: Data Management, Interoperability, and Training
Data Management in BIM
If we don’t get this part right, the other BIM applications won’t perform as they should. Data management refers to how data is collected, stored, updated, and shared. Without clear protocols for data management, multiple versions of a file can end up floating around, causing confusion and errors.
Interoperability Challenges in BIM
Interoperability in BIM refers to the seamless exchange and integration of data between different software applications and systems. This can be a challenge because different software can use different file formats and data structures, and this can quickly cause errors.
Training Challenges in BIM
Training is a critical but often overlooked aspect of BIM implementation. Inadequate training on BIM software and processes can lead to limited utilization and subpar utilization of BIM capabilities, hindering its full potentials. New hires usually enter with varying backgrounds in BIM proficiency. Therefore, training can vary drastically, and this can be really challenging, especially with budgeting and time constraints.
Key Takeaways:
- Data management is critical for the smooth application of BIM in construction projects.
- Insufficient training can hinder the successful implementation of BIM.
- The seamless exchange of data between different software is still a challenge in BIM.
Sources:
Interoperability Challenges in Building Information Modelling (ΒΙΜ)
Interoperability Analyses of BIM Platforms for Structural Project
The Future of BIM: Emerging Trends and Advancements
Key Takeaways:
- BIM mandates are driving manufacturers to comply with industry standards.
- Cloud-based technology offers accessibility, collaboration, and cost savings.
- Digital twins enable real-time monitoring and decision-making.
- BIM and prefabrication enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
- Global BIM market growth is projected to reach $15 billion by 2025.
Emerging Trends in 2024
- Interoperability and Open BIM Standards: Seamless data exchange and collaboration between different software platforms.
- Advanced Simulation and Analysis: Enhanced design optimization, energy efficiency, and structural integrity.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Automation of tasks, predictive analytics, and improved decision-making.
- Cloud-Based Collaboration: Centralized data storage, real-time updates, and remote access.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality Integration: Immersive visualization, virtual site visits, and training.
Benefits of BIM Adoption
- Improved Collaboration: Enhanced communication and coordination among stakeholders.
- Enhanced Design Coordination: Reduced risks of design conflicts and errors.
- Increased Productivity: Automated workflows, reduced rework, and faster project completion.
- Cost Reduction: Optimized design, reduced change orders, and improved efficiency.
Integrating BIM into Construction
- Define Project Goals and Scope: Clearly establish the intended uses of BIM for the specific project.
- Establish Data Standards: Define common data formats, naming conventions, and data accuracy protocols.
- Implement Technology: Select appropriate BIM software and hardware to support the project requirements.
- Train and Support Team: Provide training and support to all project stakeholders to ensure proficient BIM usage.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Regularly assess BIM implementation and make adjustments as needed to maximize its effectiveness.
Real-World Applications
- Virtual Site Tours: Conduct immersive site visits for stakeholders unable to attend the physical location.
- Predictive Maintenance: Monitor building performance and identify potential issues before they become problems.
- As-Built Documentation: Create detailed, accurate documentation of the constructed building for future reference and maintenance.
- Facilities Management: Manage building operations, maintenance, and renovations using BIM data.
Sources:
- BIMobject: The Future of BIM: 9 Trends You Can’t Ignore
- Construction Placements: The Evolution of BIM Technology: Trends and Insights for 2023
FAQ
Q1: What does BBM stand for in construction?
A1: In construction, BBM stands for Building Information Modeling (BIM).
Q2: What are the benefits of using BIM in construction?
A2: BIM offers numerous benefits, including improved project coordination, reduced errors, increased efficiency, better visualization, and enhanced decision-making.
Q3: Who is responsible for implementing and managing BIM on a construction project?
A3: The BIM Manager is responsible for coordinating stakeholders, controlling the level of information in the BIM model, and authorizing project component changes.
Q4: What are the challenges associated with BIM implementation?
A4: Challenges include project complexity, stakeholder management, data management, and the need for specialized expertise.
Q5: How is BIM transforming the construction industry?
A5: BIM is revolutionizing the industry by improving project efficiency, reducing costs, enabling better collaboration, and facilitating digitalization of construction processes.
- How to Get Rid of Mushrooms in Your Lawn: A Complete Guide - April 24, 2025
- How to Get Rid of Ground Hornets: A Safe and Effective Guide to Eliminating Nests - April 24, 2025
- How to Get Rid of German Roaches Fast: DIY Methods for Quick Control - April 24, 2025